New Delhi. 01 January 2025. 2024 witnessed some path-breaking achievements & breakthroughs as Ministry of Defence (MoD), marched ahead with renewed vigour to make India a strong, secure, self-reliant & prosperous nation, as envisioned by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi. Shri Rajnath Singh assumed the office of Raksha Mantri for the second consecutive term in June this year and under his leadership, the Ministry reaffirmed its resolve to work in the priority areas to realise the vision of self-reliance in Defence. Some of the major highlights of 2024 include:
India-China border consensus
India and China achieved a broad consensus to restore the ground situation in certain areas along the LAC. Both countries have been holding talks at diplomatic and military levels to resolve the differences in some areas along the LAC. As a result, a broad consensus was developed on the basis of equal and mutual security. Raksha Mantri, during the Chanakya Defence Dialogue on October 24, 2024, described the consensus as proof that continuous dialogue brings solutions.
Aatmanirbharta in Defence
- Positive Indigenisation List: To boost Aatmanirbharta in defence & minimise imports by DPSUs, Department of Defence Production in July, notified the fifth Positive Indigenisation List (PIL) consisting of 346 items. These include strategically-important Line Replacement Units/Systems/ Sub-systems/Assemblies/Sub-assemblies/Spares & Components and raw materials. Earlier, four PILs comprising 4,666 items were notified by the DDP for DPSUs, of which 2,972 items, having import substitution value worth Rs 3,400 crore, have already been indigenised. These five lists for DPSUs are in addition to the five PILs of 509 items notified by the Department of Military Affairs. These lists include highly-complex systems, sensors, weapons and ammunition.
- Record Defence Production: MoD achieved the highest-ever growth in indigenous defence production in value terms during Financial Year (FY) 2023-24, on the back of successful implementation of the policies and initiatives of the Government. The defence production went up to a record-high figure of Rs 1,26,887 crore, reflecting a growth of 16.7% over the defence production of the previous financial year. The value of defence production in FY 2022-23 was Rs 1,08,684 crore. Of the total value of production in 2023-24, about 79.2% has been contributed by DPSUs/other PSUs and 20.8% by the private sector. The data shows that in terms of absolute value, both DPSUs/PSUs and private sector have recorded a steady growth in defence production. MoD has set a target to achieve Rs three lakh crore defence production by 2029.
- Record Defence Exports: Defence exports touched a record Rs 21,083 crore (approx. US$ 2.63 Billion) in the FY2023-24, a growth of 32.5% over the previous fiscal when the figure was Rs 15,920 crore. The figures indicated that the exports grew by 31 times in the last 10 years as compared to FY 2013-14. The defence industry, including the private sector and DPSUs, have made tremendous efforts in achieving the highest-ever exports. The private sector and DPSUs contributed about 60% and 40% respectively. Raksha Mantri has exuded confidence that the target to export defence equipment worth Rs 50,000 crore by 2029 will be met.
- C-295 TATA Aircraft Complex: Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Spanish President Mr Pedro Sanchez jointly inaugurated the TATA Aircraft Complex for manufacturing of C-295 transport aircraft at TATA advanced systems limited Campus in Vadodara, Gujarat in October 2024. In September 2021, MoD had signed a Rs 21,935-crore contract with Airbus Defence and Space SA, Spain for supply of 56 aircraft – 16 to be brought in fly away condition from Spain and 40 to be built in India by TASL. Of the 16 aircraft, six have already been inducted into IAF at 11 Sqn based at Vadodara. The last would be delivered by August 2025. The first Made-in-India C-295 is expected to be rolled out of the Final Assembly Line facility at Vadodara by September 2026 and the remaining by August 2031.
- Indian Light Tank: Indian Light Tank (ILT) ‘Zorawar’ has achieved a major milestone by firing a number of rounds at different ranges at an altitude of more than 4200m (High Altitude Location) with consistently accurate results. This was subsequent to the Phase I trial in desert environment in September 2024. This light tank has been defined, designed and developed by Combat Vehicles Research & Development Establishment, the Chennai-based laboratory of DRDO for the Indian Army. It is manufactured by the Industry Partner Larsen & Toubro Precision Engineering & Systems.
During the field trials conducted in the desert terrain, the Light Tank demonstrated exceptional performance, efficiently meeting all the intended objectives. In the initial phase, the tank’s firing performance was rigorously evaluated and it achieved the required accuracy on designated targets.
Major Inductions/Commissioning
- INS Arighaat: The second Arihant-Class submarine ‘INS Arighaat’ was commissioned into the Indian Navy on August 29, 2024 at Visakhapatnam in the presence of Raksha Mantri. The construction of INS Arighaat involved the use of advanced design and manufacturing technology, detailed research & development, utilisation of special materials, complex engineering and highly skilled workmanship. It has the distinction of having the indigenous systems and equipment which were conceptualised, designed, manufactured & integrated by the Indian scientists, industry and Naval personnel. The technological advancements undertaken indigenously on this submarine make it significantly more advanced than its predecessor Arihant.
- INS Tushil: INS Tushil (F 70), the latest multi-role stealth-guided missile frigate, was commissioned into the Indian Navy in the presence of Raksha Mantri Shri Rajnath Singh at the Yantar Shipyard in Kaliningrad, Russia on December 09, 2024. It is an upgraded Krivak III class frigates of the Project 1135.6 of which, six are already in service – three Talwar class ships, built at Baltiysky shipyard, St. Petersburg, and three follow-on Teg class ships, built at Yantar shipyard, Kaliningrad. INS Tushil, the seventh in the series, is the first of the two upgraded additional follow-on ships, the contract for which was signed in October 2016 between JSC Rosoboronexport, Indian Navy and the Government of India. Armed with a range of advanced weapons, it is designed for blue water operations across the spectrum of naval warfare in all four dimensions – air, surface, underwater and electromagnetic.
- LCH Prachand: Induction of all Light Combat Helicopters LSP was completed in February 2024. IAF personnel were vigorously trained on the system and the LCH successfully participated in Ex Gagan Shakti in April 2024.
Major Acquisitions
To provide substantial boost to the Indian defence industry and reduce foreign spending significantly, Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) and Defence Procurement Board (DPB), during 2024 (upto November), accorded Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) for 40 Capital Acquisition proposals amounting to Rs 4,22,129.55 crore. Out of these, AoNs for Rs 3,97,584.34 Crore (i.e. 94.19 %) have been accorded to be procured from indigenous sources. These include:
- DAC, in September 2024, accorded AoN for 10 capital acquisition proposals amounting to Rs 1,44,716 crore. These include procurement of Future Ready Combat Vehicles, Air Defence Fire Control Radars, Dornier-228 aircraft, Next Generation Fast Patrol & Offshore Patrol Vessels.
- DAC, in February 2024, accorded approval for AoN for various capital acquisition proposals amounting to Rs 84,560 crore. The proposals include new generation anti-tank mines, Air Defence Tactical Control Radar, Heavy Weight Torpedoes, Medium Range Maritime Reconnaissance & Multi-Mission Maritime Aircraft, Flight Refueller Aircraft & Software Defined Radios.
- In July 2024, DAC approved capital acquisition proposals including procurement of Advanced Land Navigation System for Armoured Fighting Vehicles of the Indian Army and 22 Interceptor Boats with latest state-of-art system for the Indian Coast Guard.
- DAC, in December 2024, accorded AoN for five capital acquisition proposals amounting to over Rs. 21,772 crore. These include procurement of Water Jet Fast Attack Crafts, Fast Interceptor Craft, Electronic Warfare Suite, Next Generation Radar Warning Receiver, Advanced Light Helicopters for surveillance in coastal areas.
Major contracts
- MoD inked a contract with the US Government for Tri-Service procurement of 31 MQ-9B Sky/Sea Guardian High Altitude Long Endurance Remotely Piloted Aircraft System (RPAS) in October 2024. Another contract was signed with General Atomics Global India Pvt Ltd for Performance Based Logistics for these RPAS through Depot Level Maintenance, Repair & Overhaul in India.
- Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
- A contract was signed in September 2024 for 240 AL-31FP Aero Engines for Su-30MKI aircraft at a cost of over Rs 26,000 crore.
- A contract for procurement of 12 Su-30MKI aircraft along with associated equipment was inked in December 2024, at an approximate cost of Rs 13,500 crore.
- Two contracts for a combined value of Rs 8,073.17 crore were signed in March 2024 for acquisition of 34 Advanced Light Helicopters (ALH) Dhruv Mk III along with Operational Role Equipment for Indian Army (25 ALHs) and Indian Coast Guard (09 ALHs).
- A contract for RD-33 Aero Engines for MiG-29 aircraft was inked in March 2024 at a cost of Rs 5,249.72 crore. These aero engines will be produced by the Koraput Division of HAL
- A contract was signed in March 2024 for Mid Life Upgrade of 25 Dornier Aircraft along with associated equipment for the Indian Navy at a cost of Rs 2,890 crore.
Bharat Electronics Limited
- A contract was inked in February 2024 for procurement of 11 Shakti Electronic Warfare Systems along with associated equipment for Indian Navy under Buy (Indian-IDDM) category at a total cost of Rs 2,269.54 crore.
- Advanced Weapon Equipment India Limited
- A contract was signed in February 2024 for manufacturing & supply of a total of 463 indigenously manufactured 12.7 mm Stabilised Remote Control Guns for the Indian Navy & Indian Coast Guard at a total cost of Rs 1,752.13 crore, with Indigenous Content of more than 85%.
- Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited
- A contract was inked in January 2024 for acquisition of 14 Fast Patrol Vessels (FPVs) for the Indian Coast Guard. The value of the contract is Rs 1,070.47 crore. These multi-role FPVs will be indigenously designed, developed and manufactured under Buy (Indian-IDDM) Category.
- Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited
- In March 2024, a contract was signed for the procurement of 693 Armament Upgrades of Infantry Combat Vehicle BMP2 to BMP2M. This upgrade includes Night Enablement, Gunner Main Sight, Commander Panoramic Sight and Fire Control System (FCS) with Automatic Target Tracker under Buy (Indian-IDDM) category.
- BrahMos Aerospace Private Limited
- Two contracts were inked in March 2024 for procurement of BrahMos missiles at a cost of Rs 19,518.65 crore and Procurement of Ship borne BrahMos system at a cost of Rs 988.07 crore.
- Larsen & Toubro Limited
- Two contracts for procurement of Close-in Weapon System at a cost of Rs 7,668.82 crore, and High-Power Radar at a cost of Rs 5,700.13 crore were signed in March 2024.
- A contract was inked with Larsen & Toubro Limited in December 2024 for procurement of 155 mm/52 calibre K9 VAJRA-T Self-Propelled Tracked Artillery Guns for the Indian Army under Buy (Indian) category at a total cost of Rs 7,628.70 crore.
- Cochin Shipyard Limited
- A contract was inked in November 2024 for Short Refit and Dry Docking of INS Vikramaditya at an overall cost of Rs 1,207.5 crore.
- Chowgule & Company Private Limited
- A contract was signed in October 2024 for procurement of six Air Cushion Vehicles for the Indian Coast Guard at a total cost of Rs 387.44 crore. These amphibious vessels, also called ‘Hovercrafts’, will be procured under the Buy {Indian) category.
Defence Budget
In the Union Budget of FY 2024-25, MoD has been allocated Rs 6.22 lakh crore (approx. US $75 Billion), the highest among the Ministries. The allocation to MoD for FY 2024-25 is higher by approx. Rs one lakh crore (18.43%) over the allocation for FY 2022-23 and 4.79% more than allocation of FY 2023-24. Out of this, a share of 27.66% goes to capital; 14.82% for revenue expenditure on sustenance and operational preparedness; 30.66% for Pay and Allowances; 22.70% for Defence Pensions, and 4.17% for civil organisations under MoD. The total allocation comes out to approx. 12.90% of Budgetary Estimate of Union of India. 75 per cent of the defence capital procurement budget has been earmarked for domestic industry.
Gaganyaan Programme
The Gaganyaan Programme was launched by the Government for demonstrating Human Spaceflight capability in Low Earth Orbit, wherein, a manned spacecraft will be launched safely to LEO for an orbital mission of 5 to 7 days followed by safe re-entry and recovery on earth. The Prime Minister revealed the names of four IAF astronauts to the nation and awarded them with the ‘Space Wings’ in February 2024. The four IAF astronauts are: Group Captain Prasanth Balakrishnan Nair, Group Captain Ajit Krishnan, Group Captain Angad Pratap and Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla. Presently, Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla and Group Captain Prasanth Balakrishnan Nair are undergoing space training at NASA for Axiom-4 mission to International Space Station scheduled in 2025.
Defence Cooperation
The year saw Ministry of Defence take defence cooperation with its friendly countries to the next level through visits of the dignitaries and military exercises. Raksha Mantri, Raksha Rajya Mantri, Chief of Defence Staff, three Service Chiefs and Defence Secretary undertook visits to various nations with the aim to strengthen defence ties with them. Major events of Raksha Mantri include:
- US visit: Raksha Mantri Shri Rajnath Singh visited US from August 23 to 26, 2024. He met US Secretary of Defence Mr Lloyd Austin, during which the two Ministers held wide-ranging discussions on bilateral defence cooperation, industrial collaboration, regional security and other international issues. Raksha Mantri also met the US Assistant to the President for National Security Affairs Mr Jake Sullivan.
- Russia visit: Raksha Mantri visited Russia from December 08 to 10, 2024. He co-chaired the 21st session of the India-Russia Inter-Governmental Commission on Military & Military Technical Cooperation with his Russian counterpart in Moscow. Raksha Mantri also called on Russian President Mr Vladimir Putin in Moscow. Both leaders discussed various issues of bilateral defence cooperation, and expressed that partnership between both countries holds immense potential and combined efforts will pave way for remarkable outcomes.
- UK visit: Raksha Mantri paid an official visit to London, United Kingdom from January 09 – 10, 2024. He held a bilateral meeting with UK Defence Minister Mr Grant Shapps in London, and discussed a range of defence, security and cooperation matters with particular emphasis on enhancing defence industrial collaboration. He also called on the then Prime Minister of UK Mr Rishi Sunak, highlighting that both nations have made significant strides in moulding and recrafting the historic ties into a modern, multifaceted and mutually beneficial partnership.
- ADMM-Plus: Raksha Mantri addressed the 11th ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus) at Vientiane, Lao PDR on November 21, 2024. He reiterated India’s stand for rule-based international order for peace & prosperity in Indo-Pacific, and pitched for Buddhist doctrines of peaceful co-existence for global peace. On the sidelines, Raksha Mantri met the Defence Minister of China Admiral Dong Jun and highlighted the fact that amicable relations between India and China, would have positive implications for global peace and prosperity. He also met US Secretary of Defense Mr Lloyd J Austin, with both sides recognising remarkable progress made under US-India Defence Industrial Cooperation Roadmap. Raksha Mantri also met his Malaysian, Lao PDR, South Korean, Australian, New Zealand Philippines counterparts.
- India-Japan 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue: Raksha Mantri and External Affairs Minister Dr S Jaishankar hosted Japanese Minister of Defense Mr Kihara Minoru and Minister of Foreign Affairs Ms Yoko Kamikawa for the 3rd India-Japan 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue in New Delhi on August 20, 2024. On the sidelines of the 2+2 dialogue, a bilateral meeting was held between Raksha Mantri and his Japanese counterpart. They reviewed the existing defence cooperation activities and discussed ways to enhance further cooperation.
- India-Singapore Defence Dialogue: Raksha Mantri and Minister of Defence of Singapore co-chaired the sixth India-Singapore Defence Ministerial Dialogue in New Delhi on October 22, 2024. Both Ministers acknowledged the deep and long-standing bilateral defence relations based on shared outlook on regional peace, stability and security.
- India-Netherlands: Raksha Mantri held a bilateral meeting with the Netherlands Defence Minister Ms Kajsa Ollongren in New Delhi on February 23, 2024. Both Ministers discussed the possibilities for expanding their bilateral defence cooperation, particularly in maritime and industrial domains. They noted the increased interaction between the two Navies and expressed keenness to work together to enhance maritime security in the Indian Ocean Region.
OROP 10th Anniversary
November 07, 2024 marked the tenth anniversary of One Rank One Pension (OROP). OROP was implemented as a significant step towards addressing long-standing demand and reaffirming the nation’s gratitude to the heroes. It is a tribute to veterans and ex-service personnel who dedicated their lives in protecting the nation. Over the decade lakhs of pensioners and their families have benefitted from the landmark initiative. OROP also represents the government’s commitment to the well-being of the armed forces.
Appointments
- Rajnath Singh assumed charge as the Raksha Mantri for the second consecutive term in June 2024. “Under the leadership of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, our aim will be to further strengthen the security apparatus of the country, with focus on achieving self-reliance in defence manufacturing. Armed Forces modernisation and the welfare of the soldiers, both serving and retired, will continue to be our main focus,” he said upon his joining.
- Sanjay Seth assumed charge of the office of Minister of State, Ministry of Defence in June 2024. He said he would strive towards fulfilment of several initiatives of the Ministry of Defence aimed at strengthening the nation’s security.
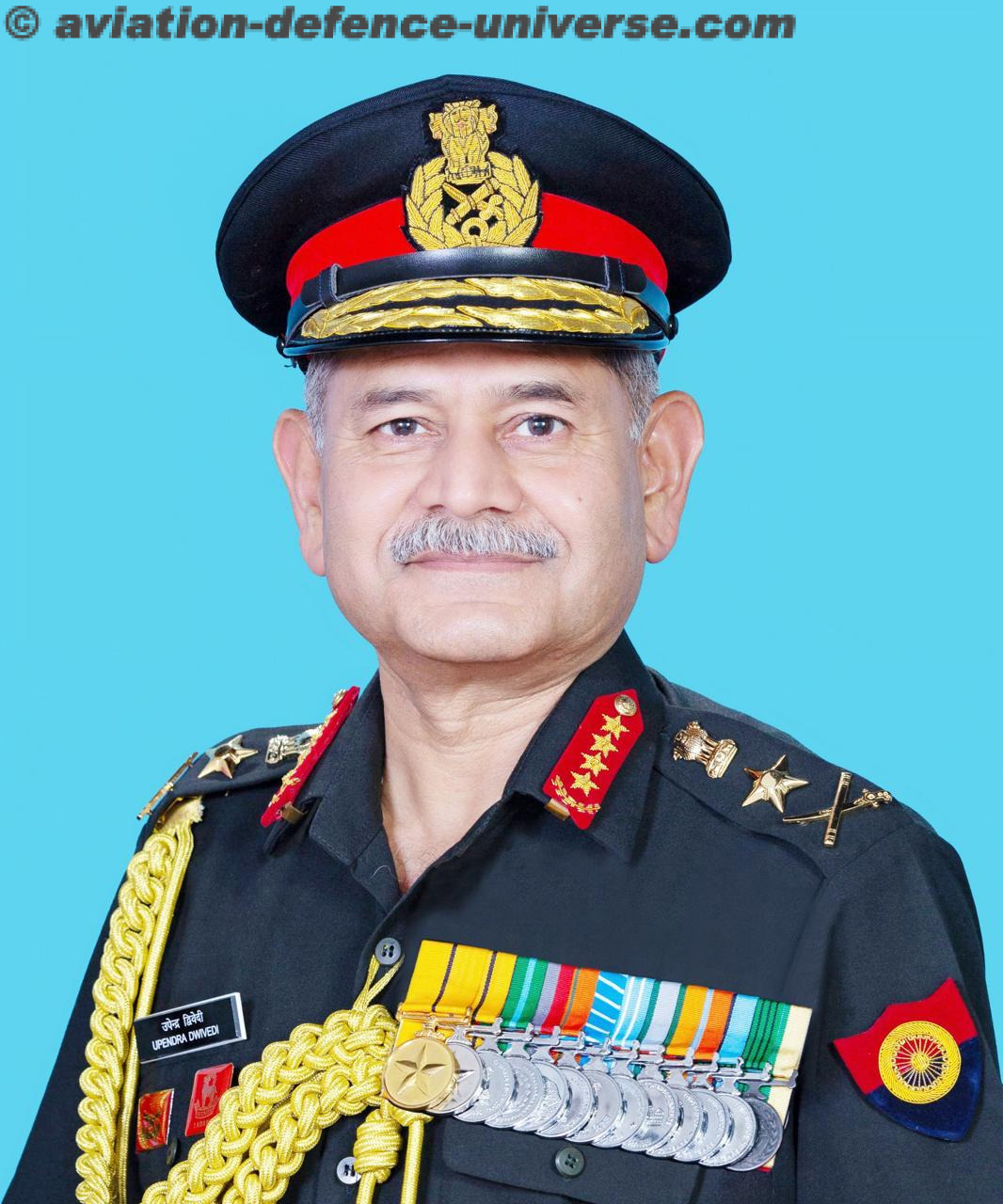
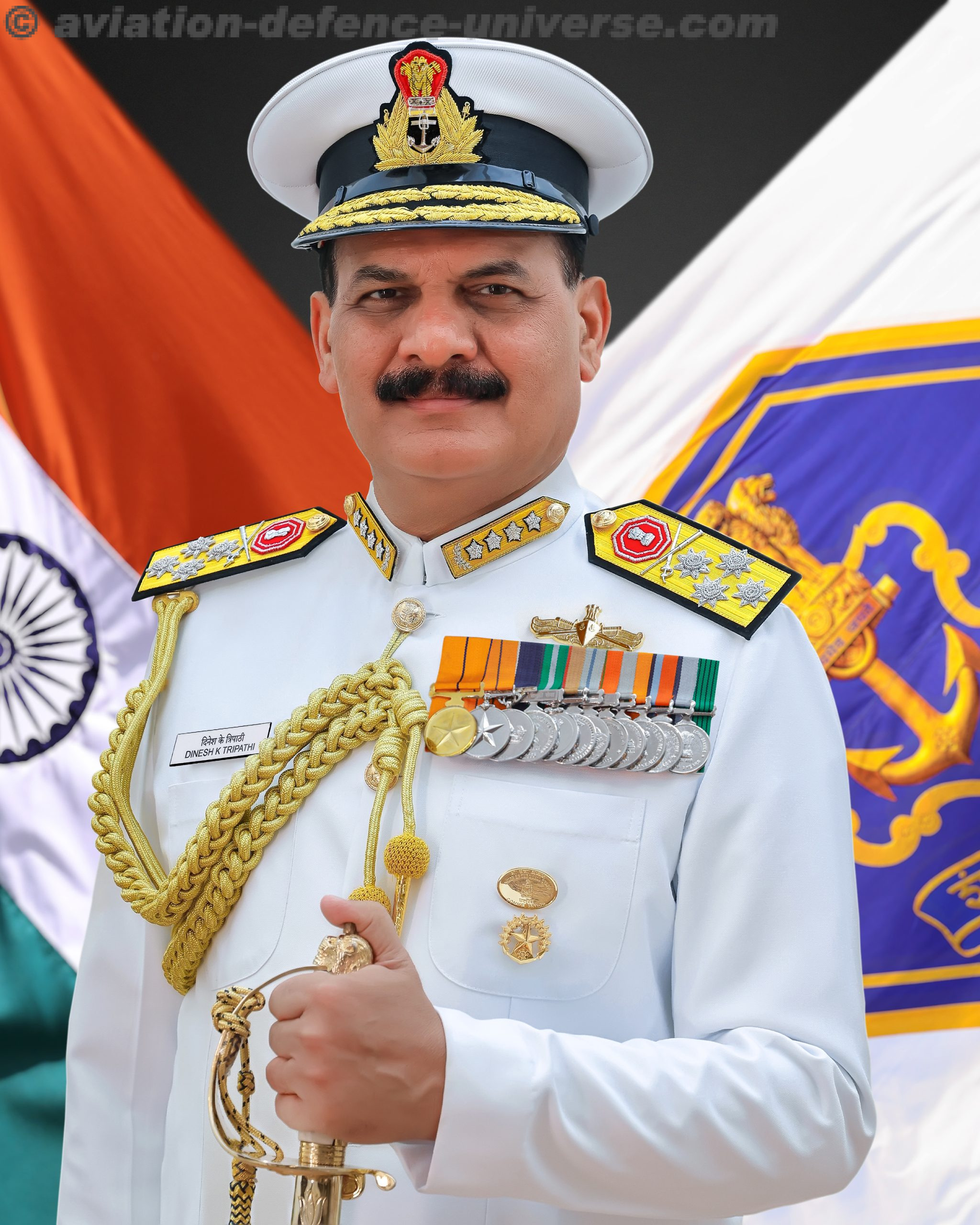
- General Upendra Dwivedi, Admiral Dinesh K Tripathi and Air Chief Marshal AP Singh took over as the Chief of the Air Staff, Chief of the Naval Staff and Chief of the Air Staff respectively this year.
- Rajesh Kumar Singh assumed the office of Defence Secretary and Shri Sanjeev Kumar took over as Secretary (Defence Production).
- DG Paramesh Sivamani took over as the 26th Director General of Indian Coast Guard.