- Home Minister Amit Shah inaugurated Indian Cybercrime Coordination Centre (I4C) in January 2020 to deal with cybercrime
- A citizen-centric National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP) is one of the most significant achievements of I4C, the portal has been used for more than 14 crore times till date, which shows its credibility and usefulness
- Through Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & Systems (CCTNS), 99.9% Police Stations (16,597) are registering 100% FIRs directly and 28.98 crore Police records have been registered
- More than 12.30 crore requests have been disposed of by the State Police, out of 12.82 crore service requests received from citizens
- National Automated Finger-Print Identification System (NAFIS) has revolutionized the fingerprint recognition system in crime control, 1,05,80,266 records are being integrated on NAFIS
- National Cybercrime Helpline number 1930, is helping the common citizen in registering online financial frauds, all States/UTs have been on boarded and more than 263 banks, e-commerce companies and others have been integrated
 New Delhi. 04 January 2024. Under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi and guidance of Union Home Minister and Minister of Cooperation Amit Shah, building a Cyber Safe India is one of the top priorities of the Ministry of Home Affairs. Government is fully committed towards creating a cyber- safe country as cyber security has become an essential aspect of all security related matters globally.
New Delhi. 04 January 2024. Under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi and guidance of Union Home Minister and Minister of Cooperation Amit Shah, building a Cyber Safe India is one of the top priorities of the Ministry of Home Affairs. Government is fully committed towards creating a cyber- safe country as cyber security has become an essential aspect of all security related matters globally.
In line with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision of a cyber-safe India, Home Minister Amit Shah inaugurated Indian Cybercrime Coordination Centre (I4C) in January 2020 to deal with cybercrime in the country in a coordinated and comprehensive manner with an outlay of Rs. 340 crore. The I4C focuses on tackling issues related to cybercrime for citizens, including improving coordination between various Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs) and stakeholders.
The efforts made by the Ministry of Home Affairs under the guidance of Home Minister Amit Shah have now started showing results, examples of which are as many. Since its roll out, I4C has been working towards enhancing the nation’s collective capability to tackle cybercrime and develop effective coordination among the Law Enforcement Agencies and stakeholders, driving change in India’s overall capability to tackle cybercrime. A citizen-centric National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP) was launched in 2019, which is one of the most significant achievements of I4C.
The portal has been used for more than 14 crore times till date, which shows its credibility and usefulness. More than 31 lakh cybercrime complaints have been reported by citizens and more than 66,000 FIRs have been registered by LEAs of States/UT so far. Through Crime and Criminal Tracking Network & Systems (CCTNS), 99.9% Police Stations (16,597) are registering 100% FIRs directly and 28.98 crore Police records have been registered. More than 12.30 crore requests have been disposed of by the State Police, out of 12.82 crore service requests received from citizens. FIRs in NCRP are reflected through CCTNS.
National Automated Finger-Print Identification System (NAFIS) of National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) has revolutionized the fingerprint recognition system in crime control, with this system, the work of tracing the involvement of interstate criminals in crimes is being done with greater ease, accuracy and efficiency across the country. 1,05,80,266 records are being integrated on NAFIS. This system will help I4C in interstate linkage of cyber criminals.
Another initiative of I4C, National Cybercrime Helpline number 1930, is helping the common citizen in registering online financial frauds. All States/UTs have been on boarded and more than 263 banks, e-commerce companies and others have been integrated. With the help of this system, more than Rs 1,100 crore of citizen’s money which was siphoned off by cyber criminals have been saved, thus, benefitting more than 4.3 lac victims in 3 years through CFCFRMS module. This system is integrated with NPCI for real time prevention. We will be on boarding more banks through API integration. Further, Rs 12.12 crore have been released to 28 States / UTs under ‘HM’s Contingency Reserve’ for setting up the infrastructure of National Helpline no.1930 in the March, 2023. National Helpline no.1930 receives around 50,000 calls every day. In 2023, using this CFCFRMS module, 12.32 % of total fraudulent amount was lien marked against 6.73 % in 2021, this shows the impact of National Helpline number 1930 and CFCFRMS module.
| Year | % Lien Amount | Amount (in Crore) |
| 2021 | 6.73 | 36.38 |
| 2022 | 7.35 | 169.04 |
| 2023 | 12.32 | 921.59 |
As a part of Prevention Strategy, I4C accords high priority to blocking the communication and financial infrastructure abused by criminals. It proactively identifies and facilitate blocking of SIM cards, IMEI Devices, Bank Accounts, UPI IDs, Websites & URLs and Malicious Mobile Applications.
I4C is instrumental in Blocking of more than 2,95,000 fake SIM cards, more than 46,000 IMEI, more than 2800 websites/URLs, 595 Mobile Applications through its module JCCT Management Information System (JMIS) (Beta version).
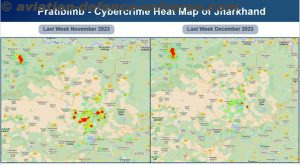
The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) and Joint Cybercrime Coordination Teams (JCCT) Jamtara, Jharkhand has launched the ‘Pratibimb’ platform which not only aggregates data but also employs geospatial mapping to pinpoint the physical locations of mobile numbers associated with cybercrimes. This innovative web platform is set to redefine the way Law Enforcement Agencies tackle online criminal activities, offering a powerful new tool in the ongoing battle against digital threats. Over 400 arrests have been made in last one month by Jharkhand Police. There are concrete evidences of decline in offences committed from this area. This model will be expanded nationally to eliminate hotspots.
An analytical report on modus operandi of top 50 cyber-attacks have been prepared.Massive Open Online Courses (MOOC) platform, namely ‘CyTrain’ was launched for capacity building of Police officers by I4C, MHA under its vertical i.e. National Cybercrime Training Centre (NCTC). More than 52,000 Certificates have been issued to Police officials after successful completion of training. Further, over 1,15,000 Government officials have successfully completed “Stay Safe in Cyber Space” course on IGOT Karmayogi platform.
National Cyber Forensic Laboratory (NCFL) has been established for investigation purposes at Delhi. Assistance in investigation have provided in more than 9000 cyber and digital forensic cases to States/UTs and Central Law Enforcement Agencies. Under Cyber Crime Prevention against Women and Children (CCPWC) Scheme, Rs. 122.24 crore have been released to States/UTs for establishing Cyber Forensic cum Training Lab, Training LEAs and Judicial officials and Hiring of Jr Cyber Forensic Consultants.
More than 178 Advisories of cyber-crimes have been shared by I4C with States/UTs, Ministries/Departments as a preventive measure and the same are available at www.cyberpolice.nic.in. In consultation with States/UTs, I4C has constituted seven Joint Cyber Crime Coordination Teams (JCCTs) for inter State coordination among Law Enforcement Agencies of States/UTs. Further, 7 JCCT workshops were convened in 2023 at Hyderabad, Ahmedabad, Guwahati, Vishakhapatnam, Lucknow, Chandigarh and Ranchi. I4C also provides inputs to JCCTs at regular intervals. Interstate linkages of mobile and IMEI of cyber criminals are also sent to State Police authorities at frequent intervals under JMIS Module (Beta Version) of I4C, MHA.
Real time investigation training Cyber Cells from across the country join for the weekly peer learning session over Virtual platform every Friday at 4:00 PM to learn from their peers. Best practices, operational experience, challenges faced, and success stories are shared in the session followed by questions and answers. 38 such Peer Learning sessions have been organized by I4C, MHA in last 38 weeks in which Police officials from over 350 locations participate.
One of the vertical of I4C, National Cybercrime Ecosystem Management Unit is coordinating with various stakeholders as a “Whole of Government Approach” for creating mass awareness in cyber hygiene for prevention of cybercrime, effective coordination and recommending policy inputs to reduce the cybercrime at policy level.
The social media handle “CyberDost”, which provides cyber safety tips at regular intervals is available on various social media handles viz. X, Facebook, Instagram, Telegram, LinkedIn, KOO, Public App, WhatsApp, YouTube and Share Chat. Over 1 million followers are present across all platforms. More than 2,000 social media post and more than 200 short videos on cyber safety tips have been created and circulated across social media platforms till date.
States/UTs and Ministries of Government of India have been requested by MHA to organize “Cyber Jaagrookta (Awareness) Diwas” on first Wednesday of every month at 11 am on cyber hygiene and launch mass awareness in vernacular languages for all schools and colleges.
A Cyber Volunteer Framework for utilizing the services of citizens by concerned Police authorities of States/UTs has been provided on NCRP. States/UTs may like to enrol Cyber Volunteers for dissemination of cyber hygiene across the country. Union Home Minister also flagged off the Cyber Volunteers Squad from 07 Premier Educational Institutions of India during the G20 Conference on “Crime and Security in the age of NFTs, AI and Metaverse” which was held from 13th-14th July, 2023 at Gurugram.
The major cybercrime Modus Operandi reported in India in 2023 were highlighted which are Part Time Job Fraud/Ponzi scheme, illegal Lending Apps, Customer Care Number & Android Malware, Account Takeover/ Impersonation, Sextortion, etc. I4C has also provided technical support to States/UTs in some of the major crackdown of cybercrime.

















































































































