By Maj Gen LB Chand, VSM (Retd.)
New Delhi. 15 August 2024. There is no sense of bewilderment or even an iota of dispute when communications are the nervous system that control and coordinate the functioning of each and every battlefield entity; be it teeth, solar-plex or the tail.
 Modern day digital battle space, relies heavily on robotics, Artificial Intelligence, unmanned platforms as weapon delivery systems, smart projectiles to firstly shape, attain superiority and ultimately win the battle. In today’s battle field courage of soldiers continues to be the primary battle winning factor. But the nature of warfare has changed. Contactless battles from standoff distance softens the target (physical space; ground/air/sea/outer-space, cyberspace or cognitive) for the ground forces to firstly, occupy then protect & dominate. Air and sea forces to facilitate occupation and subsequently dominate and protect. An integrated Battle Space demands coordinated application of all war resources from all domains at the centre of gravity. It holds true, without exceptions, that the communication network are the connectors, coordinators, controllers, applicators and protectors of all resources (in cyber space).
Modern day digital battle space, relies heavily on robotics, Artificial Intelligence, unmanned platforms as weapon delivery systems, smart projectiles to firstly shape, attain superiority and ultimately win the battle. In today’s battle field courage of soldiers continues to be the primary battle winning factor. But the nature of warfare has changed. Contactless battles from standoff distance softens the target (physical space; ground/air/sea/outer-space, cyberspace or cognitive) for the ground forces to firstly, occupy then protect & dominate. Air and sea forces to facilitate occupation and subsequently dominate and protect. An integrated Battle Space demands coordinated application of all war resources from all domains at the centre of gravity. It holds true, without exceptions, that the communication network are the connectors, coordinators, controllers, applicators and protectors of all resources (in cyber space).
A technological superiority in Artificial Intelligence, cyber & virtual space and Green Technology has overwhelming significance in becoming a global technology power and nullifying Technology Denial as a Deterrence. These technology verticals are building blocks of modern weapon systems. Superiority in these now have matching importance to that of superiority in Air/ Land / Sea. The former has significantly more relevance during peace times. Interestingly as per the Global Finance Magazine rankings of 2023 on “Most Technology Advanced Nations” South Korea, USA and Taiwan are 1st, 2nd and 3rd respectively. China is at 38th position and India 62nd1. China is 6.86 and India 12.01 scores behind the leader; South Korea. India must partner with South Korea, USA, Taiwan and Israel (6th) as their strategic technology development partners under Atmanirbharta.
Flagging these aspects was of importance since the above mentioned three technology determinant / identifiers are the foundations of Modern Digital Battle field and directly influence Information Communication Technology, Cyber and AI. The paramount question is “How well prepared are Indian Armed Force’s ICT infrastructure in all battle spaces”? This article addresses this all important moot question.
 A Peep into the Journey so Far – Corps of Signals have always been a step ahead of the communication requirements in terms of reach, capacity, availability and reach. Indian Army ICT infrastructure is primarily classified into two broad categories. First, a robust backbone in the form of ASCON (Army Static Switched Communication Network) and NFS (Network for Spectrum). These are currently a mix of ATM and NGN OTN with GPON. Second, a tactical network comprising of mil-hardened International Mobile Communications (IMT), Upgraded AREN, Portable Satellite Communications, IP Based NETCONC (Net Connect Centres), tactical data radios, IP Radio based backhauls etc. The existing ICT infrastructure at the core and edge is robust and adequately meets the requirements of modern digital battle apace. When one take a holistic view of access or last mile ICT infrastructure it has some limitations in terms of omni-presence, speed of deployment, capacity and latency.
A Peep into the Journey so Far – Corps of Signals have always been a step ahead of the communication requirements in terms of reach, capacity, availability and reach. Indian Army ICT infrastructure is primarily classified into two broad categories. First, a robust backbone in the form of ASCON (Army Static Switched Communication Network) and NFS (Network for Spectrum). These are currently a mix of ATM and NGN OTN with GPON. Second, a tactical network comprising of mil-hardened International Mobile Communications (IMT), Upgraded AREN, Portable Satellite Communications, IP Based NETCONC (Net Connect Centres), tactical data radios, IP Radio based backhauls etc. The existing ICT infrastructure at the core and edge is robust and adequately meets the requirements of modern digital battle apace. When one take a holistic view of access or last mile ICT infrastructure it has some limitations in terms of omni-presence, speed of deployment, capacity and latency.
In operationally important areas the capacities have been built up. Effectiveness and efficiency of Operation Administration and Management (OAM) of ICT to match the pace of intense battle has some inadequacies. OAM mismatch not only leads to mismatch in operational time lines but also adds to the fatigue of both (wo)man and ICT infrastructure. Sustainability of such an ICT infrastructure is a suspect during intense battle. An integrated testing of ICT infrastructure to assess its robustness and effectiveness must be done without any further delay. The services as well as IT traffic can easily be simulated with the help of traffic and service generators. This simulated exercise would give a near realistic picture of ITC infrastructure’s effectiveness & robustness in an integrated battle space (Air, Land, Sea and Cyber).
 Major Operational Voids – Emergency and one time procurements to address the voids in ICT infrastructure meet the immediate requirements in terms of capacity. But, a major residual void would still exist in terms of matching ICT’s rollout/ stability/ capacity with the operational time lines of battle space entities. The complexity increases when these entities (ops, int & surveillance and logistics) are of different services (IA, IAF and IN or even Homeland Security Forces). A common tri-service overarching OAM that takes care of security, authentication/ authorisation and data sharing is an unavoidable immediate operational necessity. AI and robotics has made technological superiority a battle winning factor in modern day warfare.
Major Operational Voids – Emergency and one time procurements to address the voids in ICT infrastructure meet the immediate requirements in terms of capacity. But, a major residual void would still exist in terms of matching ICT’s rollout/ stability/ capacity with the operational time lines of battle space entities. The complexity increases when these entities (ops, int & surveillance and logistics) are of different services (IA, IAF and IN or even Homeland Security Forces). A common tri-service overarching OAM that takes care of security, authentication/ authorisation and data sharing is an unavoidable immediate operational necessity. AI and robotics has made technological superiority a battle winning factor in modern day warfare.
On the Anvil – The ICT Information Structure road map of each service is well defined. Perspective Planning and Force Development is taking place based upon these plans. Army specific design and architecture of agile low foot print Tactical Communication have been made. These are in advanced stages of implementation and trials. NFS and ASCON Phase- 4 along with corresponding AFNet of IAF and NEWN and Satellite Communications of IN are at advanced stages of implementation and are available. Network Operating Centres (NOCs) and Security Operating Centres (SOCs) continue to operate in service specific unavoidable silos. However, there is a need to have a tri-service NOC/ SOC that caters to the needs of tri-service integration of the resources in an integrated digital battle and cyber space. Many next generation communication systems that exploit and explore optical, quantum and Cyber-RF are being developed under National Research and Development initiatives. ICT infrastructure and these R&D initiatives will pave the path for an AI assisted military force of the not so distant future.
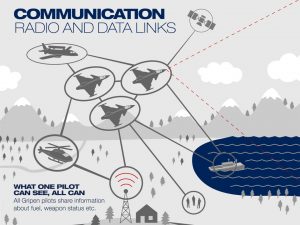 Conclusions – No force can act in isolation in a battle space. Land, Air, Sea, Space and Cyber are indistinguishable as far as tenets of modern warfare goes. The operational, logistics and Intelligence / Surveillance entities employed in these dimensions may vary however they have commonality in objective and purpose. They can no longer operate in silos. While service specific ICT infrastructure is being rolled out there is a need for integration of these into a common digital space. Tri-service OTN core of NFS that interconnects access networks of each service is a major step in integration of service-specific network. There is a need to bring about viable integration of OAMs to provision a common cyber and virtual space to all end users.
Conclusions – No force can act in isolation in a battle space. Land, Air, Sea, Space and Cyber are indistinguishable as far as tenets of modern warfare goes. The operational, logistics and Intelligence / Surveillance entities employed in these dimensions may vary however they have commonality in objective and purpose. They can no longer operate in silos. While service specific ICT infrastructure is being rolled out there is a need for integration of these into a common digital space. Tri-service OTN core of NFS that interconnects access networks of each service is a major step in integration of service-specific network. There is a need to bring about viable integration of OAMs to provision a common cyber and virtual space to all end users.
(Maj Gen L B Chand, VSM, Retd is a retired Corps of Signal Officer. As Project Director of ASCON he setup the ASCON Phase-III network. He has been associated with design and test-bedding of communications for Indian Army Tac C3I systems. The views expressed are personal. He can be contacted on editor.adu@gmail.com)


































































































































